This product is no longer available and has been replaced by: SI-111SS. Some accessories, replacement parts, or services may still be available.

| Services Available |
|---|
Overview
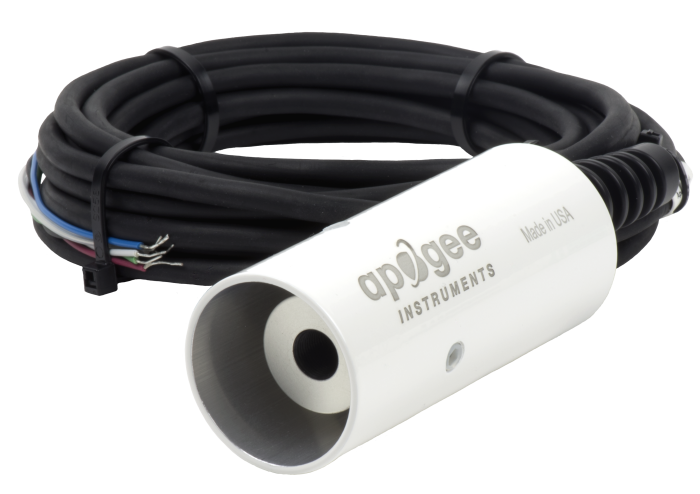
The SI-111, manufactured by Apogee, is a precision infrared radiometer that determines the surface temperature of an object without physical contact. It measures both the subject's surface temperature and the sensor-body temperature. A Campbell Scientific datalogger uses these measurements to calculate the correct temperature of the subject.
Read More
Benefits and Features
- Compatible with most Campbell Scientific data loggers
- Measures surface temperature continuously in the field
- Provides road surface, plant canopy, soil surface, snow surface, and water surface temperature measurements
- Avoids influencing the temperature, providing more accurate measurements
- Ideal for providing spatial averages
- Rugged construction—two temperature probes housed in an aluminum body with a germanium window
Images





Detailed Description
The SI-111 consists of a thermopile, which measures surface temperature, and a thermistor, which measures sensor body temperature. The two temperature sensors are housed in a rugged aluminum body that contains a germanium window.
Both the thermopile and the thermistor output a millivolt signal that most of our data loggers can measure. The data logger uses the Stefan-Boltzman equation to correct for the effect of sensor body temperature on the target temperature. The corrected readings yield an absolute accuracy of ±0.2°C from -10° to +65°C.
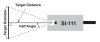
Field of View (FOV)
The SI-111 has a 22-degree half-angle field-of-view (FOV). The FOV is reported as the half-angle of the apex of the cone formed by the target (cone base) and the detector (cone apex). The target is a circle from which 98% of the radiation viewed by the detector is being emitted.
Note: Prior to November 2008, the SI-111 was named the IRR-P.
Compatibility
Please note: The following shows notable compatibility information. It is not a comprehensive list of all compatible products.
Dataloggers
| Product | Compatible | Note |
|---|---|---|
| 21X (retired) | ||
| CR10 (retired) | ||
| CR1000 (retired) | ||
| CR10X (retired) | ||
| CR200X (retired) | ||
| CR211X (retired) | ||
| CR216X (retired) | ||
| CR23X (retired) | ||
| CR300 (retired) | ||
| CR3000 (retired) | ||
| CR310 | ||
| CR500 (retired) | ||
| CR5000 (retired) | ||
| CR510 (retired) | ||
| CR6 | ||
| CR800 (retired) | ||
| CR800 (retired) | ||
| CR850 (retired) | ||
| CR850 (retired) | ||
| CR9000 (retired) | ||
| CR9000X (retired) |
Additional Compatibility Information
Mounting
The SI-111 is often fastened to a CM200-series crossarm, a tripod or tower mast, or a user-supplied pole using a CM230, CM230XL, or CM220 mount. The CM230 and CM230XL are adjustable inclination mounts that allow the SI-111 to be mounted perpendicular to the target surface when the target surface is on an incline. The CM230XL is similar to the CM230, but the CM230XL places the SI-111 further from the pole or crossarm. The SI-111 may also be attached directly to a user-supplied camera tripod.
Specifications
| Input Power | 2.5 V excitation (for thermistor) |
| Response Time | < 1 s (to changes in target temperature) |
| Target Temperature Output Signal | 60 μV per °C difference from sensor body |
| Body Temperature Output Signal | 0 to 2500 mV |
| Optics | Germanium lens |
| Wavelength Range | 8 to 14 μm (corresponds to atmospheric window) |
| Field of View (FOV) | 22° half angle |
| Operating Temperature Range | -55° to +80°C |
| Operating Relative Humidity Range | 0 to 100% RH |
| Cable Description | 4.5 m (14.76 ft) twisted, shielded 4-conductor wire with Santoprene casing, ending in pigtails |
| Absolute Accuracy |
|
| Uniformity |
|
| Repeatability |
|
| Diameter | 2.3 cm (0.9 in.) |
| Length | 6 cm (2.4 in.) |
| Weight | 190 g (6.7 oz) |
Documents
Frequently Asked Questions
Number of FAQs related to SI-111: 8
Expand AllCollapse All
Case Studies
Overview In the fight against climate change, innovative solutions are emerging to address the global challenge......read more
This case study discusses the integration of CPEC310 and AP200 systems to explore the theories......read more
The Problem—How to optimize green-roof performance The University of Toronto's Green Roof Innovation Testing Laboratory (GRIT......read more
Networks using the ALERT protocol are designed to give immediate access to data that indicates......read more
The cultivation and export of roses and other flowers is a huge business in Colombia.......read more
Privacy Policy Update
We've updated our privacy policy. Learn More




