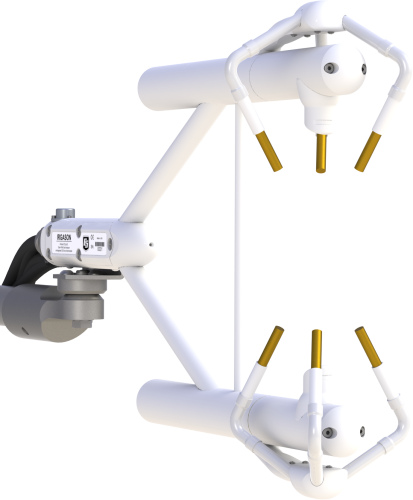
Gas analyzer and sonic anemometer in one sensor






Overview
Campbell Scientific’s IRGASON® fully integrates the open-path analyzer and sonic anemometer. Designed specifically for eddy-covariance carbon and water flux measurements, the patented design is easier to install and use than separate sensors and provides increased measurement accuracy. The IRGASON® simultaneously measures absolute carbon dioxide and water vapor, air temperature, barometric pressure, three-dimensional wind speed, and sonic air temperature. U.S. patent D680455
For more information about the benefits of having a colocated measurement, refer to the poster "Improved eddy flux measurements by open-path gas analyzer and sonic anemometer co-location."
Read More
Benefits and Features
- New conformal coating helps protect sonic transducers in corrosive environments
- Combined support structure causes less flow distortion than two separate sensors
- Truly colocated gas analyzer and sonic anemometer measurements avoid flux loss due to sensor separation
- Synchronized gas analyzer and sonic anemometer measurements avoid the need to correct for time lag
- Low power consumption; suitable for solar power applications
- Measurements are temperature compensated without active heat control
- Low noise
- Maximum output rate of 60 Hz with 20 Hz bandwidth
- Angled windows shed water and are tolerant to window contamination
- Field rugged
- Field serviceable
- Factory calibrated over wide range of CO2, H2O, pressure, and temperature in all combinations encountered in practice
- Extensive set of diagnostic parameters
- Fully compatible with Campbell Scientific dataloggers; field setup, configuration, and field zero and span can be accomplished directly from the datalogger
- Sonic temperature determined from three acoustic paths; corrected for crosswind effects
- Innovative signal processing and transducer wicks considerably improve performance of the anemometer during precipitation events
EasyFlux® DL is a free CRBasic program for Campbell open-path eddy-covariance systems that is available in the Downloads section. To learn more about EasyFlux® DL, visit the software product's web page.
Images
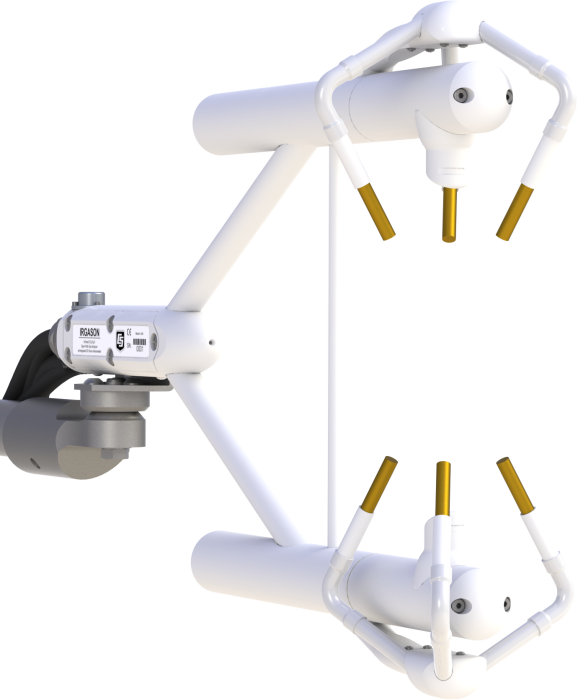

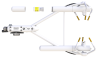
Detailed Description
The IRGASON® has the following outputs:
- Ux (m/s)
- Uy (m/s)
- Uz (m/s)
- Sonic Temperature (°C)
- Sonic Diagnostic
- CO2 Density (mg/m3)
- H2O Density (g/m3)
- Gas Analyzer Diagnostic
- Ambient Temperature (°C)
- Atmospheric Pressure (kPa)
- CO2 Signal Strength
- H2O Signal Strength
- Source Temperature (°C)
Specifications
| Patent | U.S. Patent No. D680455 |
| Operating Temperature Range | -30° to +50°C |
| Calibrated Pressure Range | 70 to 106 kPa |
| Input Voltage Range | 10 to 16 Vdc |
| Power | 5 W (steady state and power up) at 25°C |
| Measurement Rate | 60 Hz |
| Output Bandwidth | 5, 10, 12.5, or 20 Hz (user-programmable) |
| Output Options | SDM, RS-485, USB, analog (CO2 and H2O only) |
| Auxiliary Inputs | Air temperature and pressure |
| Warranty | 3 years or 17,500 hours of operation (whichever comes first) |
| Cable Length | 3 m (10 ft) from IRGASON® to EC100 |
| Weight |
|
Gas Analyzer |
|
| Path Length |
15.37 cm (6.05 in.) A temperature of 20°C and pressure of 101.325 kPa was used to convert mass density to concentration. |
Gas Analyzer - CO2 Performance |
|
| -NOTE- | A temperature of 20°C and pressure of 101.325 kPa was used to convert mass density to concentration. |
| Accuracy |
|
| Precision RMS (maximum) |
0.2 mg/m3 (0.15 μmol/mol) Nominal conditions for precision verification test: 25°C, 86 kPa, 400 μmol/mol CO2, 12°C dewpoint, and 20 Hz bandwidth. |
| Calibrated Range | 0 to 1,000 μmol/mol (0 to 3,000 μmol/mol available upon request.) |
| Zero Drift with Temperature (maximum) | ±0.55 mg/m3/°C (±0.3 μmol/mol/°C) |
| Gain Drift with Temperature (maximum) | ±0.1% of reading/°C |
| Cross Sensitivity (maximum) | ±1.1 x 10-4 mol CO2/mol H2O |
Gas Analyzer - H2O Performance |
|
| -NOTE- | A temperature of 20°C and pressure of 101.325 kPa was used to convert mass density to concentration. |
| Accuracy |
|
| Precision RMS (maximum) |
0.004 g/m3 (0.006 mmol/mol) Nominal conditions for precision verification test: 25°C, 86 kPa, 400 μmol/mol CO2, 12°C dewpoint, and 20 Hz bandwidth. |
| Calibrated Range | 0 to 72 mmol/mol (38°C dewpoint) |
| Zero Drift with Temperature (maximum) | ±0.037 g/m3/°C (±0.05 mmol/mol/°C) |
| Gain Drift with Temperature (maximum) | ±0.3% of reading/°C |
| Cross Sensitivity (maximum) | ±0.1 mol H2O/mol CO2 |
Sonic Anemometer - Accuracy |
|
| -NOTE- | The accuracy specification for the sonic anemometer is for wind speeds < 30 m s-1 and wind angles between ±170°. |
| Offset Error |
|
| Gain Error |
|
| Measurement Precision RMS |
|
| Speed of Sound | Determined from 3 acoustic paths (corrected for crosswind effects) |
| Rain | Innovative signal processing and transducer wicks considerably improve performance of the anemometer during precipitation events. |
Basic Barometer (option -BB) |
|
| Total Accuracy |
|
| Measurement Rate | 10 Hz |
Enhanced Barometer (option -EB) |
|
| Manufacturer | Vaisala PTB110 |
| Total Accuracy | ±0.15 kPa (-30° to +50°C) |
| Measurement Rate | 1 Hz |
Ambient Temperature |
|
| Manufacturer | BetaTherm 100K6A1IA |
| Total Accuracy | ±0.15°C (-30° to +50°C) |
| EC100 ingress protection | IP65 |
Documents
Manuals
Technical Papers
Miscellaneous
- Improved Flux Measurements from Campbell Scientific Open-Path Gas Analyzers: Utilizing Sonic Temperature to Account for Spectroscopic Effects on CO2 Density
- Influence of Open-path Gas Analyzer Flow Distortion on Ultrasonic Wind Measurements
- High-Frequency Air-Temperature Fluctuations for Spectroscopic Corrections
- Benefits of Having a Co-Located Measurement
- Using Molecular Sieve to Zero Infrared Gas Analyzers for Eddy Covariance or Atmospheric Profile Measurements
Downloads
EasyFlux DL for CR6OP v.2.01 (98.2 KB) 21-07-2022
CR6 datalogger program for Campbell open-path eddy-covariance systems.
EC100 OS v.8.02 (560 KB) 14-10-2019
EC100 Operating System.
Watch the Video Tutorial: Updating the EC100 Operating System.
ECMon v.1.6 (10.7 MB) 29-03-2016
EC100-Series Support Software.
Device Configuration Utility v.2.32.01 (47.7 MB) 15-04-2025
A software utility used to download operating systems and set up Campbell Scientific hardware. Also will update PakBus Graph and the Network Planner if they have been installed previously by another Campbell Scientific software package.
Supported Operating Systems:
Windows 11 or 10 (Both 32 and 64 bit)
Frequently Asked Questions
Number of FAQs related to IRGASON: 21
Expand AllCollapse All
-
Selecting which barometer to use is the choice of the user. There is a direct correlation between the accuracy level of the barometer and its cost.
- The basic barometer has an accuracy of ±1.5 kPa between 0° and 50°C. Below 0°, the error increases linearly to ±3.7 kPa at -30°C.
- The enhanced barometer offers an accuracy of ±0.15 kPa (-30° to +50°C).
When choosing a barometer, consider the effect of pressure accuracy on flux calculations. For sensible heat flux, the barometric pressure is used to calculate the density of air, which directly scales the sensible heat flux. Therefore, if the barometric pressure measurement is off by 1%, then the sensible heat flux will be off by 1%.
For CO2 flux, the EC150 and IRGASON® report CO2 as density. Thus, the barometric pressure is not used to directly calculate the flux. However, error in pressure measurements could cause an error in CO2 flux resulting from a CO2 span. During the span procedure, the user enters the “true CO2 value” as a CO2 concentration, which is later converted to density using the barometric pressure. Consequently, the error in CO2 measurements is directly proportional to the error in the barometric pressure measurement.
-
The factory calibration accounts for CO2 and H2O signal strengths down to 0.7. Therefore, to ensure quality data, windows should be cleaned before signal strengths drop below 0.7.
-
The EC150 and IRGASON® gas analyzer windows are polished, slanted at an angle, and coated with a hydrophobic material to prevent water from collecting on their surfaces. Wicks may also be used on the windows to promote capillary action and move water away from the window edges. Also, heaters in the snouts may be turned on to help minimize data loss because of precipitation and condensation events.
-
The power requirement for the IRGASON® or EC150 with CSAT3A is 5 W at room temperature regardless of whether it is powering up or under steady-state operation. At extreme cold or hot temperatures, the power requirement reaches 6 W.
-
Factory recalibration is done on an as-needed basis. When diagnostic flags begin to appear and persist even after cleaning the analyzer and verifying its settings, a recalibration is needed. Additionally, if the performance of the analyzer has degraded, a recalibration is recommended.
One performance test is to check the absolute signal strength drift over the course of 1 year. Drift of a few percent per year is normal. If the annual signal strength drift is excessive, or if the signal strength is below 0.7 when the windows are clean, a factory recalibration is needed. Furthermore, if the ratio of the CO2 to H2O signal strength is not close to one, it may also be time for a factory recalibration.
-
The barometer and temperature sensor are needed because the IRGASON® and EC150 have been calibrated at the factory over a range of temperatures (-30° to +50°C) and barometric pressures (70 to 106 kPa).
-
The minimum height for the IRGASON® or EC150 should be approximately 2 m. Sensor placement below that height may result in a significant loss in frequency response. The maximum height depends on the available upwind fetch or footprint area. As a general guideline for unstable boundary layer conditions, the height of the sensor should be less than the distance from the sensor to the outermost edge of the footprint area divided by one hundred. For example, if there is 500 m of available upwind fetch, the IRGASON® or EC150 should not exceed a height of 5 m. Note that for neutral and stable conditions, the footprint area will grow.
-
Campbell Scientific recommends replacing the scrubber bottles yearly. However, if the zero and span coefficients for the CO2 and H2O have drifted excessively, they may need to be replaced more often.
-
Yes. A fine-wire thermocouple, such as a FW05, can be used.
-
The EC150 and IRGASON® can report a negative water concentration if enough liquid water accumulates on the optical windows. This is because the absorption spectrum of liquid water differs from that of water vapor. Typically, large rain droplets do not cause this phenomenon. Rather, misty or condensing conditions, which create a water film across the entire optical window, can cause this phenomenon. After the water film evaporates, the former measurement accuracy will be restored.
The IRGASON® and EC150 may also experience some amount of drift over time. If conditions are relatively dry and it has been a long time since a zero and span has been performed on the analyzer, it is possible to report a negative water vapor concentration. In this situation, perform a zero and span of the analyzer.
Case Studies
Understanding the spatial variability of the Earth’s atmospheric boundary layer—including the surface layer near the......read more
Overview In the fight against climate change, innovative solutions are emerging to address the global challenge......read more
The Utah Geological Survey, supported by the Utah Division of Water Rights, has constructed a......read more
The Wolf Creek Dam near Jamestown, Kentucky, was constructed partially as a regular concrete hydroelectric......read more
Articles and Press Releases
Privacy Policy Update
We've updated our privacy policy. Learn More






